Automotive relays are key components of automotive electrical systems. Automotive lighting, wipers, starters, air conditioners, electric seats, electric doors and windows, anti lock braking devices, suspension controls, audio systems, etc. require relays. They are one of the most commonly used electronic components in automobiles, among which electromagnetic relays are the earliest and most widely used type of relay. What are they and how do they work? In this article, we will enter the world of automotive relays and explore their working principles and common uses.
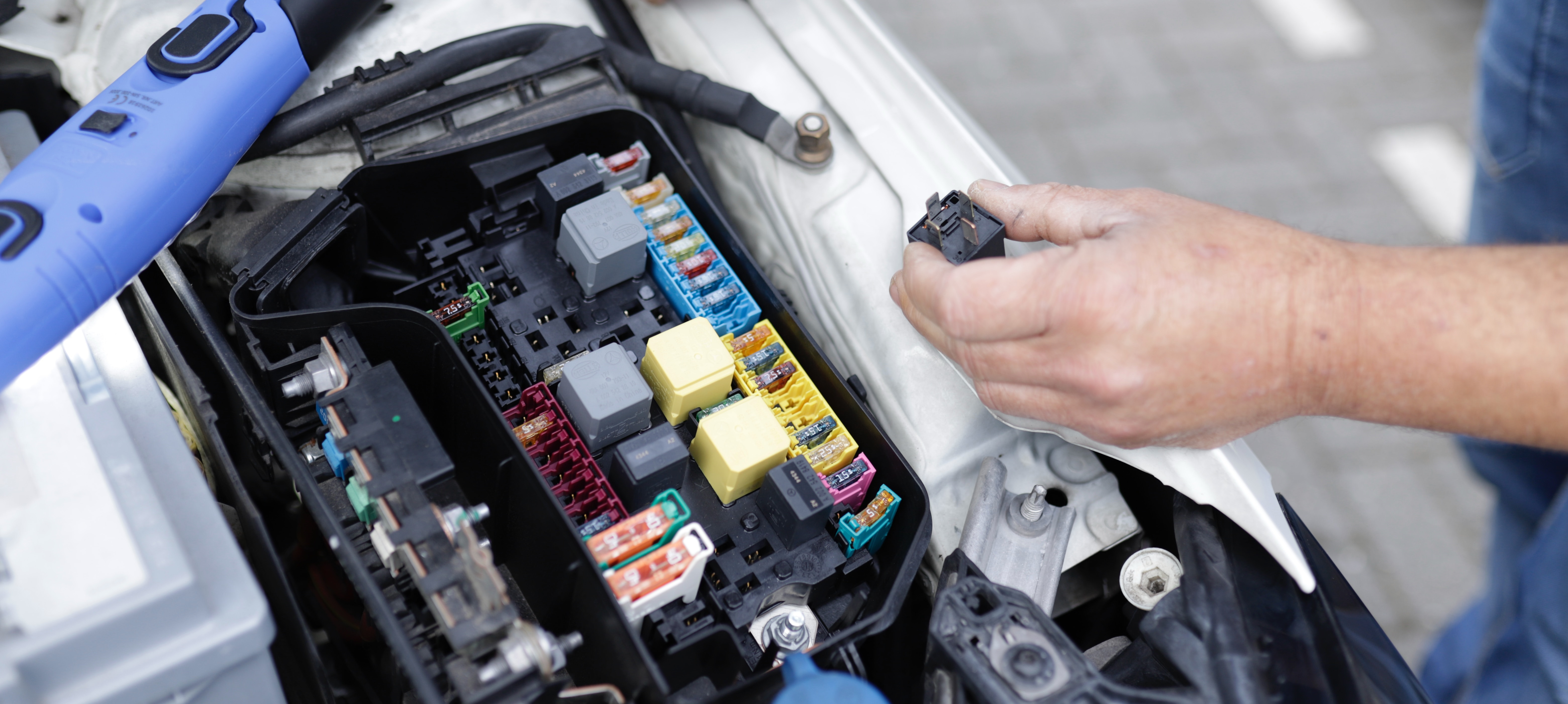

Automotive relays are widely used control switches that control large currents with low currents while protecting the switches. Essentially, it allows for controlling larger power loads with smaller electrical signals. Due to the high amount of current required, switches such as horns, starters, headlights, etc. can easily cause electric shock and erosion. If there is a relay, only a small amount of current passing through the control switch is less likely to cause erosion of the switch. So, we often say that relays are the bridge between low-power circuits and high-power circuits.
Automotive relays are essential because they allow the use of smaller and lower-capacity switches and wires in automotive control circuits. This can reduce the load on car wiring harnesses and switches, and prevent overheating and electrical damage. In addition, the position of the relay can be closer to the components it controls, thereby minimizing voltage drop on the wires.
Automotive relays are generally composed of Iron Core, Coil, YOKE, Armature, Spring, Contact, etc. the contacts are divided into Moving Contact and Fixed Contact (Stationary Contact). According to the type of contact, relays are generally divided into two types:
1. Make & Break Relay
It is also known as SPST (Single-Pole, Single-Throw). There are 4 pins (or terminals) on the body with one high current circuit and contact. The contact is opened or closed depending on whether the relay is at rest or energized.
● NC: If the contact is closed when the relay is in a stationary state, the relay is called Normally Closed.

● NO: If the contact opens when the relay is in a stationary state, the relay is called Normally Open. These relays are the more common type.
The following figure shows the internal structure of the Changeover Relay.
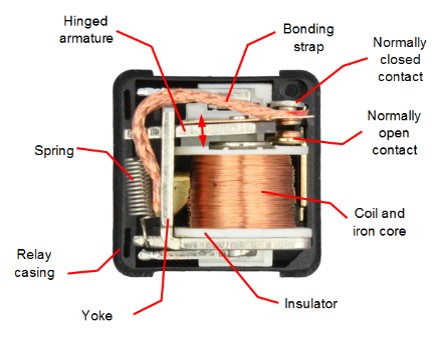
The following figure illustrates the working process of the relay. For ease of understanding, an attractive electromagnetic relay is provided here. In any type of automotive relay, the main components are the coil, armature, and contact. A wire is wound around the magnetic core, forming an electromagnet. When supplying power to the coil, it will be energized and generate an electromagnetic field. An armature is a movable component whose main function is opening or closing contacts. It is attached with a spring, so under normal working conditions, the armature returns to its original position.
1. Power-Up State
If a power source powers the coil, the relay's electromagnetic coil is energized and generates a magnetic flux proportional to the current flowing through it. This magnetic field attracts the armature to the electromagnet, so the moving and stationary contacts are close to each other, as shown in the following figure. When the relay is energized, the NO terminal contacts while the NC contact remains floating.
2. Power-Off State
When there is no power supply to the relay electromagnetic coil, no magnetic flux is generated, so the armature is in a stationary position. Therefore, both contacts remain unchanged and there is a small air gap between these contacts. In other words, NC contacts come into contact with each other when the coil is powered off.
Automotive relays have multiple uses, including:
Starter: Starting the motor requires a large amount of current to start the engine. The relay allows the ignition switch to control this high current load.
Headlights: Relays are usually used to control the headlights, ensuring that they receive sufficient power and preventing voltage drops that can cause the lights to dim.
Fuel pump: The fuel pump requires a large amount of current to deliver fuel to the engine. The relay ensures that it receives the necessary power.
Horn: Car horns require a large amount of current. The relay allows the horn button to control the horn.
It can be said that automotive relays are unsung heroes in the automotive industry. They provide a practical and effective way to manage the current in a car, allowing you to power high-current components without overloading the electrical system. Typhoenix offers a wide range of automotive relays to protect your car.
Any questions, feel free to Contact us now:

Website: https://www.typhoenix.com

Email: info@typhoenix.com

Contact: Vera

Mobile/WhatsApp: +86 15369260707

Post time: Aug-29-2023


